Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

I think you’re looking for something like the below. Laravel makes it pretty easy to perform seeding , a seeder class contains a run method by default. You can insert data by using a query builder or Eloquent model factories
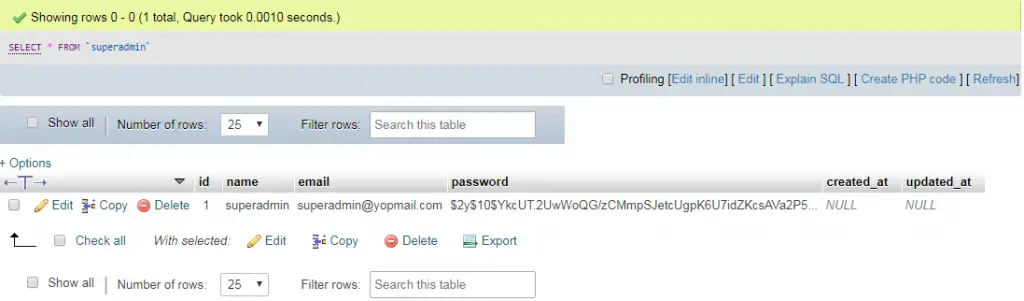
In this tutorial i will show you how to store your data into database using seeder for testing, we have a super admin table where we can store the super admin credentials.
Step 1: Create table super admin for inserting credentials:
<?php
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema;
use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint;
use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration;
class CreateSuperadminTable extends Migration
{
/**
* Run the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function up()
{
Schema::create('superadmin', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->bigIncrements('id');
$table->string('name');
$table->string('email');
$table->string('password');
$table->timestamps();
});
}
/**
* Reverse the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function down()
{
Schema::dropIfExists('superadmin');
}
}
After making migration run this command:

Step 2: After this we make a seeder name superadmin seeder for inserting record and save into database:
Now you can see the file database/seeds/SuperadminSeeder.php:
Now define your table name and insert testing data into the SuperadminSeeder
<?php
use Illuminate\Database\Seeder;
class SuperadminSeeder extends Seeder
{
/**
* Run the database seeds.
*
* @return void
*/
public function run()
{
DB::table('superadmin')->insert([
'name' => "superadmin",
'email' => 'superadmin@yopmail.com',
'password' => bcrypt('12345678'),
]);
}
}
Step 3: After following these steps call your Seeder into databaseseeder.php file , here you can see:
<?php
use Illuminate\Database\Seeder;
class DatabaseSeeder extends Seeder
{
/**
* Seed the application's database.
*
* @return void
*/
public function run()
{
$this->call(SuperadminSeeder::class);
}
}
Step 3: Now finally your seeder is ready for testing now: