Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

In this tutorial, I will give you an example of Get data from two models in Laravel, So you can easily apply it with your laravel 5, laravel 6, laravel 7, and laravel 8 application.
First, what we’re doing here, This is the example :
Sometimes we have no relationship between two models and we have no foreign key to relate two models.
We have two options to Get data from different models, The first one is to use 2 foreach loops in the Blade file, and the second one is to Merge these models in the controller and get data using only a single variable.
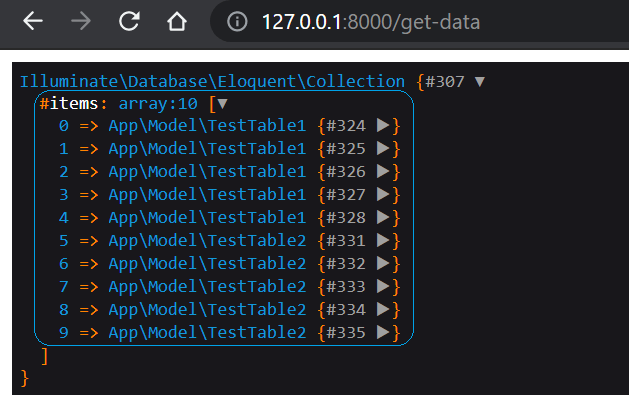
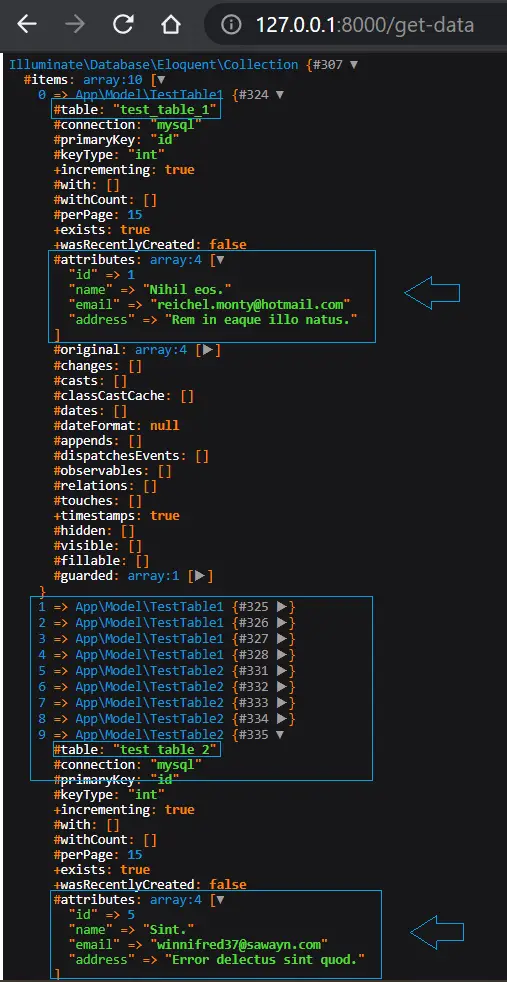
In this article, we simply concat Two different Models and get all the data of both Models, It Will Returns an array of Collections.
Let’s create migration for Two tables using the artisan command in our Terminal.
php artisan make:migration create_test_table_1_tablephp artisan make:migration create_test_table_2_tableNow we have Two migration files test_table_1 and test_table_2.
<?php
use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration;
use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema;
class CreateTestTable1Table extends Migration
{
/**
* Run the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function up()
{
Schema::create('test_table_1', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->id();
$table->string('name');
$table->string('email');
$table->string('address');
});
}
/**
* Reverse the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function down()
{
Schema::dropIfExists('test_table_1');
}
}
<?php
use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration;
use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema;
class CreateTestTable2Table extends Migration
{
/**
* Run the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function up()
{
Schema::create('test_table_2', function (Blueprint $table) {
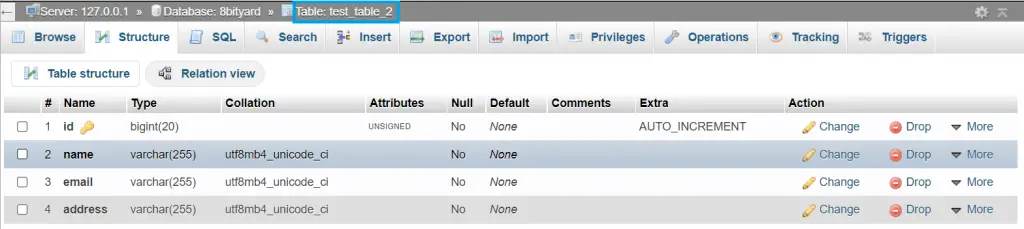
$table->id();
$table->string('name');
$table->string('email');
$table->string('address');
});
}
/**
* Reverse the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function down()
{
Schema::dropIfExists('test_table_2');
}
}
php artisan:migrate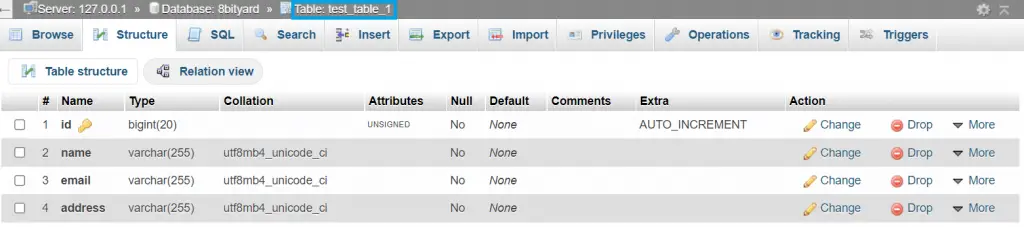
Now we create Two Models for different Tables.
php artisan make:model Model/TestTable1php artisan make:model Model/TestTable2App\Model\TestTable1
<?php
namespace App\Model;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class TestTable1 extends Model
{
protected $table = 'test_table_1';
}
App\Model\TestTable2
<?php
namespace App\Model;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class TestTable2 extends Model
{
protected $table = 'test_table_2';
}
If you have already Data in both Tables, So this is good for you, Otherwise, we store some Dummy Data using Database Seeder in these Tables.
Recommended Article :
Quickly Generate Data using Faker and Tinker
database\seeds\DatabaseSeeder
<?php
use Illuminate\Database\Seeder;
use Faker\Factory as Faker;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\DB;
class DatabaseSeeder extends Seeder
{
/**
* Seed the application's database.
*
* @return void
*/
public function run()
{
$faker = Faker::create();
foreach(range(1,5) as $index)
{
DB::table('test_table_1')->insert([
'name' => $faker->text(10),
'email' => $faker->unique()->email(10),
'address' => $faker->text(40),
]);
DB::table('test_table_2')->insert([
'name' => $faker->text(10),
'email' => $faker->unique()->email(10),
'address' => $faker->text(40),
]);
}
// $this->call(UsersTableSeeder::class);
}
}
php artisan db:seedNow we have 5-5 Entries in Both Tables.
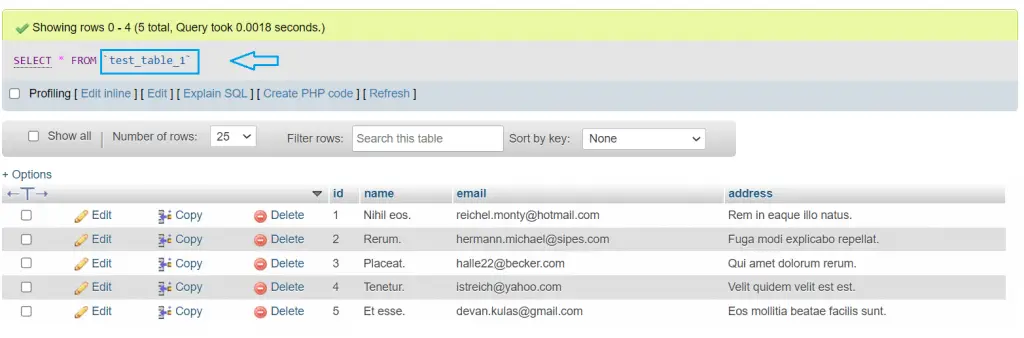
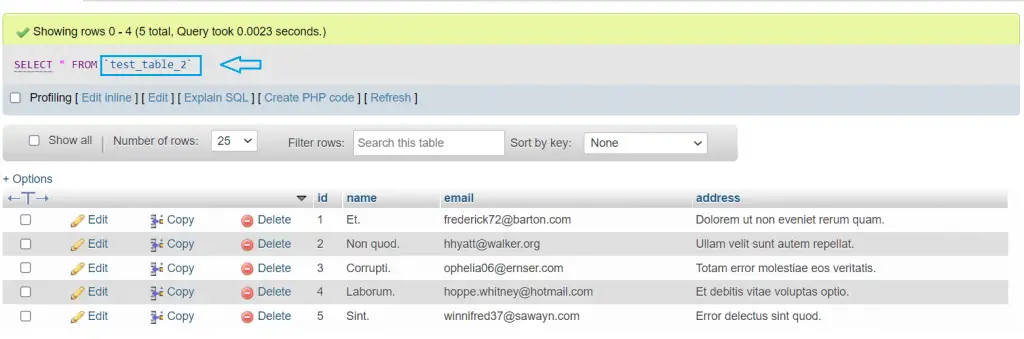
php artisan make:controller TestControllerroutes\web.php
#Example of Collection Array Merge
Route::get('get-data','TestController@index')->name('get.data');App\Http\Controllers\TestController
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use App\Model\TestTable1;
use App\Model\TestTable2;
class TestController extends Controller
{
public function index(){
$Table1_Data = TestTable1::get();
$Table2_Data = TestTable2::get();
$data = $Table1_Data->concat($Table2_Data); //Return array of Collections
dd($data);
}
}
Run your Laravel application in your Terminal.
http://127.0.0.1:8000/get-dataYou can see the output in the given below images, We have data of Test Table1 and Test Table2 Models.


In this article, we learned “How to get data from two models in Laravel”, I hope this article will help you with your Laravel application Project.