Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

In this tutorial, I will give you an example of “How to Write Logics In Model In Laravel 9”, So you can easily apply it to your Laravel 9 application.
So, let’s start from scratch to Move Controller Logic in the Model in Laravel 9 :
Generating Migration with Model :
php artisan make:model Post -mMigration Structure :
<?php
use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration;
use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema;
return new class extends Migration
{
/**
* Run the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function up()
{
Schema::create('posts', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->id();
$table->string('title');
$table->string('slug');
$table->Text('content');
$table->timestamps();
});
}
/**
* Reverse the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function down()
{
Schema::dropIfExists('posts');
}
};Run Migration :
php artisan migrate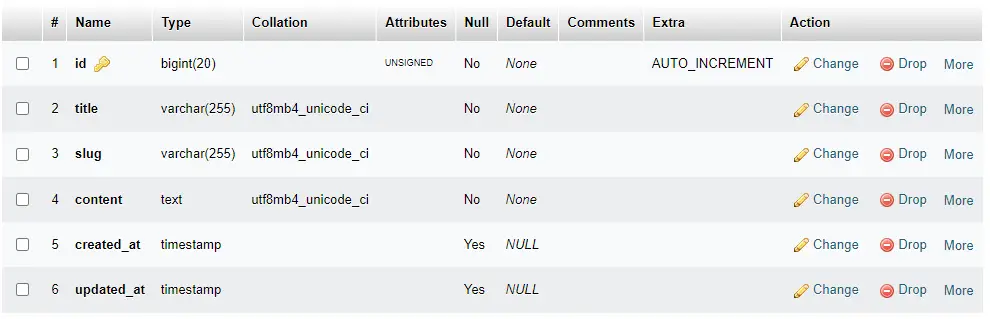
routes\web.php :
<?php
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Route;
use App\Models\Post;
/*
|--------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Web Routes
|--------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
| Here is where you can register web routes for your application. These
| routes are loaded by the RouteServiceProvider within a group which
| contains the "web" middleware group. Now create something great!
|
*/
#Write Logics In Model Example
Route::get('/create-post',[Post::class,'create']);
Route::post('/store-post',[Post::class,'store'])->name('store.post');
app\Models\Post.php
<?php
namespace App\Models;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Factories\HasFactory;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Casts\Attribute;
use Illuminate\Support\Str;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
class Post extends Model
{
use HasFactory;
#Create Post
public function create(){
return view('post.create');
}
#Generate Slug from Title
public function title() : Attribute {
return new Attribute(
set: fn($value) => [
'title' => $value,
'slug' => Str::slug($value)
]
);
}
#Store Post
public function store(Request $request){
$post = new Post();
$post->title = $request->title;
$post->content = $request->content;
$post->save();
return 'success';
}
}
resources\views\post\create.blade.php :
<div class="container">
<div class="row justify-content-center">
<div class="col-lg-8">
<div class="main">
<h3 style="background-color:powderblue;">How to Write Logics In Model in Laravel 9 - Example</h3>
<form action="{{ route('store.post') }}" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
@csrf
<div class="form-group">
<label for="title">Title<span class="text-danger">*</span></label>
<input type="text" name="title" class="form-control" required>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="content">Content<span class="text-danger">*</span></label>
<input type="text" name="content" class="form-control" required>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<button type="submit" class="btn btn btn-info">Save Post</button>
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
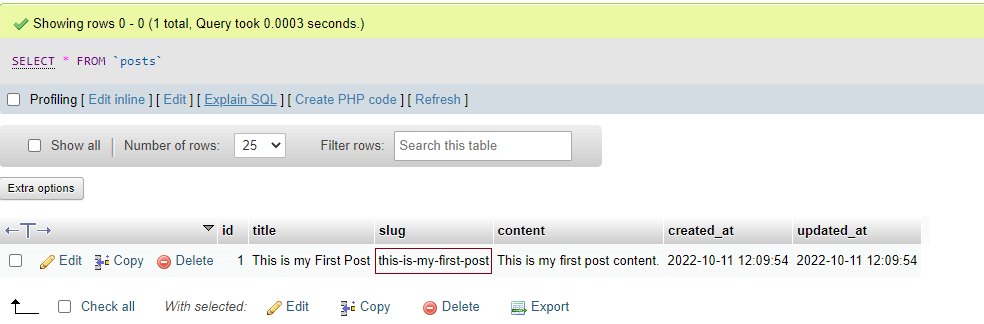
Output:-
In this article, we learned “How to Write Logics In Model In Laravel 9”, I hope this article will help you with your Laravel application Project.
Also Read:- How to Use Service Class In Laravel.